SEO WordPress a combination very powerful for any successful course of your website in Google’s organic searches. A large part of your website’s success in search comes from the decisions you make very early on. And it is a fact that you achieve this with a CMS like WordPress, which for years remains one of the most famous blogging platforms. Below are some things to think about when you start building your websites and optimizing your WordPress site:
1. Find a reliable hosting provider for your WordPress
In general, the better the hosting, the faster your content is served to your users. And this is especially important now that Core Web Vitals have become a ranking factor, and improving speed is improving ranking. There are many variables that go into the quality of hosting, but the main question is whether the hosting is shared or managed. Shared hosting is when a group of websites all share the same server. This means you can access whatever server capacity is left over from other sites. And if you don’t have enough server capacity, your site’s performance will drop dramatically. Managed hosting is when your website is guaranteed a certain server capacity. In addition, managed hosting usually comes with a bunch of additional benefits, such as a CDN, an SSL certificate, frequent backups, and a support service to take care of the technical stuff. To be fair, using shared hosting is rarely a problem for small websites, so managed hosting isn’t necessary for everyone. But, if you want peace of mind or are building a larger site, you should definitely consider managed hosting.
2. Activate an SSL security certificate
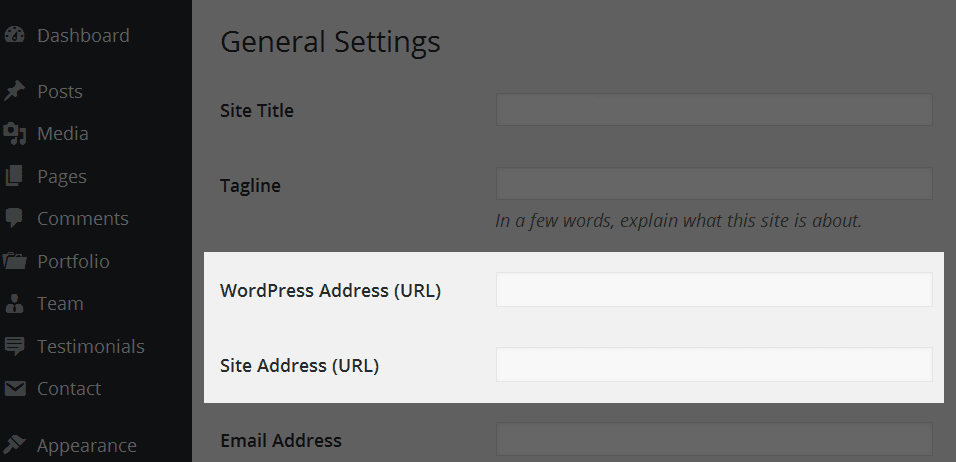
In 2014, Google added HTTPS to the list of ranking factors. It’s not one of the most important ranking signals, but HTTPS can give you a small boost in rankings. Unlike most of the other CMS platforms, WordPress does not provide an SSL certificate. The easiest way to get an SSL certificate is probably from your hosting provider. These days, most hosting companies offer a free SSL certificate, which is sometimes enabled by default and other times you have to enable it manually. So your best bet is to go to your hosting control panel and look for SSL certificate settings. After making sure your SSL certificate is enabled, you need to change your website address from http to https. To do this, open your WordPress dashboard and go to Settings > General. In the WordPress Address (URL) and Website Address (URL) fields, fill in your website’s homepage URL with https:
That’s it, now your WordPress site will be seen by Google as safe to visit.
3. Use an SEO-friendly URL structure for your WordPress pages
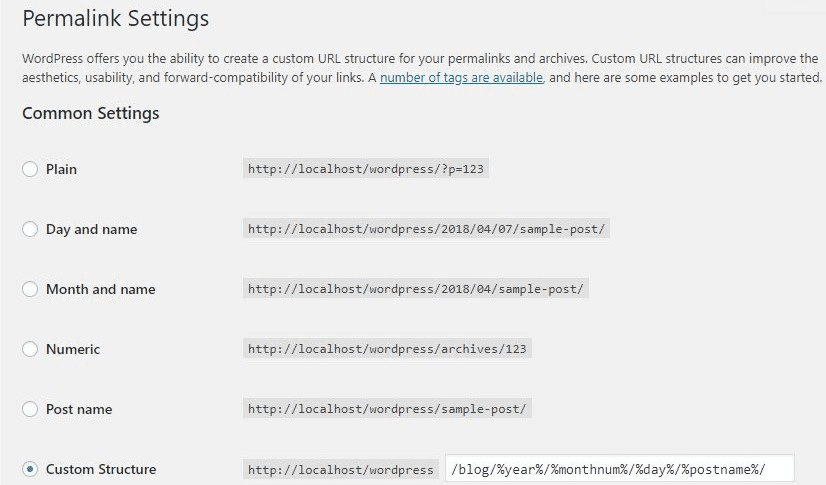
WordPress offers a few templates for your URL structure, as well as the option to create a custom URL template. Once you choose a template, it will be used on your site:
Note that most of these URL templates are not really SEO friendly. The simple template is not descriptive and misses the opportunity to use keywords in the URL. This way users can’t read your URLs and neither can search engines, so it’s also a user experience problem. Using a date in your URL is also a bad idea. Blog posts are often updated at a later date, such as the top 10 meditation apps to use in 2020 becoming the top 10 meditation apps to use in 2021 and so on. But if you have a date in your URL, you can’t really do that and you’ll have to redirect the article to a new URL. In the end, I would recommend using the Post Name URL template for your WordPress site, as it is descriptive and not restrictive, unlike other URL options in the menu.
4. Choose an SEO friendly WordPress site theme
WordPress comes with thousands of free and paid themes and most of them are very attractively designed. But behind this facade, a theme can be loaded with unnecessary code or poorly responsive to mobile screens or have almost no customization options. And until these things come to light, changing a subject will become a big hassle. For this purpose, it is best to start with a theme that has many reviews and has many sales. Some of the most popular SEO-friendly WordPress themes include Divi, OceanWP, and Astra. However, if you want to use a different theme, a good idea is to go to the theme demo and run it through Google’s web.dev tool for a quick check: Obviously, once you use the theme on your site, customize it and populate it with your own content, it will perform differently than the control. However, make sure the audit doesn’t throw up any major red flags.
5. I’m sparing with WordPress plugins
As a general rule, the fewer plugins you install on your WordPress site, the better. Remember that there is usually an external alternative for most WordPress plugins. For example, if you want to optimize your images, you can do it with an electronic compressor or a desktop editor. Shape markup can be added with the Google Markup Utility. And most of your SEO can be done with tools like Rank Tracker and WebSite Auditor. Now, of course, you can’t avoid them completely, but at least you can carefully check the plugins to choose the lighter alternatives. Limited use of plugins is unlikely to hurt your performance in a measurable way. Especially if they are well made and come from reputable developers. When it comes to SEO, some of the most popular plugins include Yoast SEO , All-in-one SEO Pack , and Rank Math .
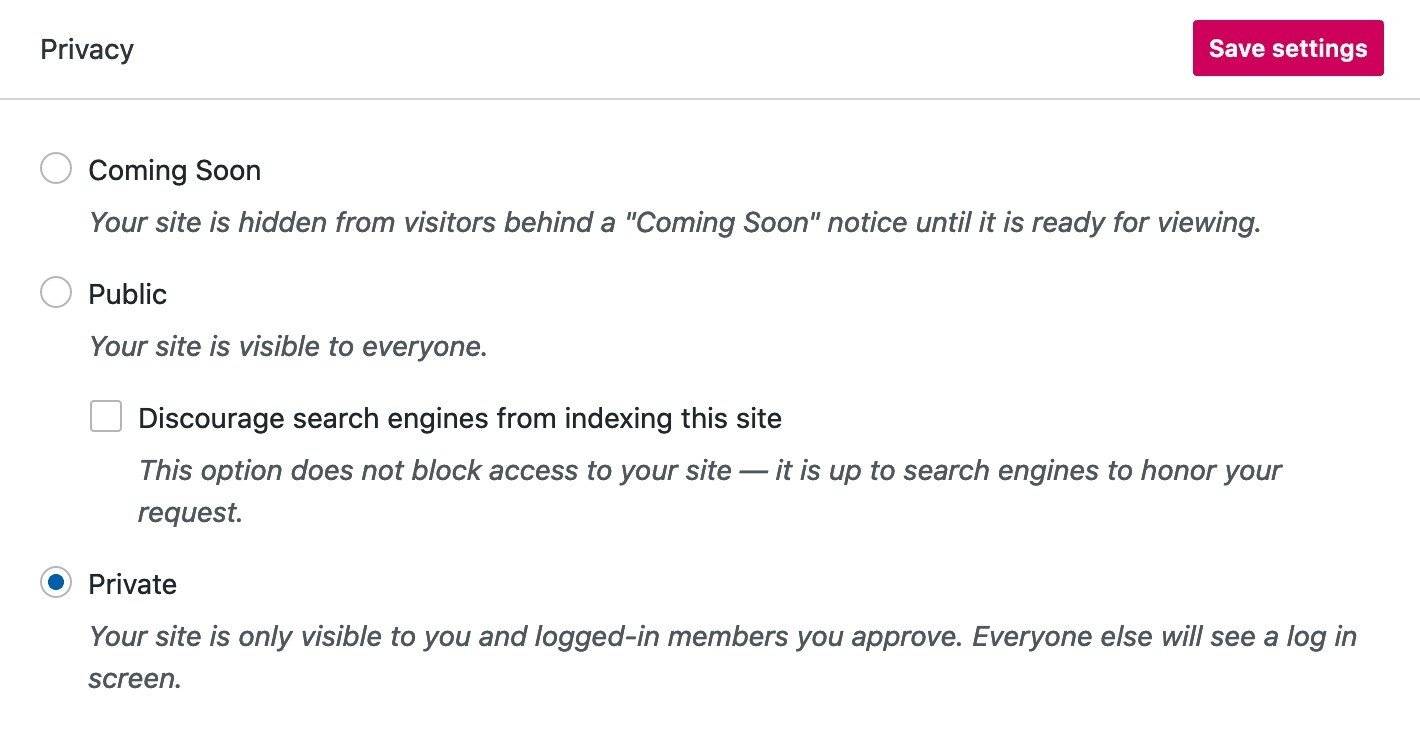
6. Check your visibility settings
As you prepare to launch your site, don’t forget to change your visibility settings. All new sites are set to Upcoming by default and will only be visible when you officially launch them from the admin panel ( >General> Privacy ):
It is also common to use public, restricted indexing settings during the development stage so that the site draft can be easily shared among stakeholders. If this is your case, be sure to allow indexing once you’re ready to share your site with search engines. Google Search Console is the ultimate tool for monitoring and improving your Search performance.
It has several categories of search reports, covering performance, indexing, user experience, search improvements, and security. To sign up for Google Search Console, visit the tool and submit your website URL. Google will provide you with a verification tag, which you will need to copy and add to your website code. To add the tag in WordPress, go to My Site(s) Tools > Marketing > Traffic> , scroll down to the Site Verification Services section, paste the code in the Google section and click in Storage. Now go back to GSC, click Verify and Google will be able to find the tag on your WP site.
8. Create and upload your sitemap
WordPress does not generate XML sitemaps. You can use one of the plugins to add this functionality. Google XML Sitemaps is probably the most widely used and trusted solution. When choosing a sitemap plugin, make sure it allows you to do the following things:
- Include/exclude user-defined URLs.
- Include/exclude WordPress taxonomies.
- Set detection priority.
- Change detection frequency.
Whatever plugin you end up using, it’s likely that it automatically generates your sitemap every time you create or remove a page on your site. The sitemap is also likely to be saved using this URL: www.example.com/sitemap.xml . Although Google will likely find your sitemap on its own, you can be sure by going to the Google Search Console, going to the > Sitemaps Index and adding your sitemap URL to the index.
9. Perform on-page SEO
Once you’ve set up your website, it’s time to populate it with content. Here are some things to keep in mind when creating new pages on your WordPress site.
Find high potential keywords
First and foremost, you need to find the keywords to build your content around. And not just any keywords, but the ones that are most likely to deliver organic traffic. This means keywords that are frequently searched for by users, but are not yet being abused by your competitors. Now, there are many keyword research tools out there, but I would recommend finding the tool that has the most research methods together.
Use < headers>
Headlines are important as both ranking signals and user experience factors. They divide the page into sections, making navigation easier and keeping users engaged. It’s also a good place to use those keywords we just discovered in the previous part. To add a heading in WordPress, click the Add Heading button or simply type /heading in the input window:
WordPress allows up to six levels of headings, although the <H1> is generally reserved for the page title and there is rarely a need to go beyond it <H4>, so we recommend organizing your pages using headings <H2> for the main sections and < H3> headings for subsections.
Add title tag and meta description
The title tag and meta description are what you see in a search snippet. By default, WordPress does not allow you to set these parameters when creating a post. All you’re allowed to create is a page title and a snippet, but these aren’t tagged with the proper HTML tags, so they’re not the same as the title tag and meta description. So, technically, Google is free to create your search snippet from anything it finds on the page. If you want a little more control over what’s included in your search snippet, you can use a plugin, probably Yoast, to edit your page title and metadata description. In Yoast, you can choose to edit a snippet and set a title and description that will be different from what you have set as a title and a snippet in your WordPress admin: Both the title tag and the meta description are a great opportunity to use some of your keywords. The title is where the main keyword is used for the page, while the description is best left for a few variations of keywords.
Add alt text for images
Although not its primary function, alt text describes the content of the image to the search engine. Alternative images are often neglected by content creators, but they can go a long way in getting your images into image search results and improving the relevancy of your content in general. To add alt text in WordPress, go to the Alt text section of the block editor when adding an image to a page. Alt texts are meant to be short, dry and descriptive rather than keyword-laden. Useful article: SEO Optimization: The 7 Steps to Rank in Google
10. Optimize your images
Image optimization has always been a part of SEO, but it has become especially urgent now that Core Web Vitals judges pages based on speed. One of the vital ones, Largest Contentful Paint, is particularly concerned with images, as images tend to be the largest pieces of content on any page. Therefore, the faster your images load, the better your page rank. The obvious way to make images load faster is to make them lighter, ie compress them and use appropriate image formats. If you want to go a step further, you can also defer images off-screen and work on efficient encoding. Within WordPress, most of these tasks can be accomplished with an image optimization plugin. Commonly recommended plugins include WP Smush, Imagify and reSmush.it. Although, if you have a relatively small site and don’t need to edit a ton of images, I recommend choosing an external tool for image optimization. Online tools like TinyJPG and TinyPNG will very well compress your images to about half their original size.
11. Apply Schema markup
If you are not familiar with Schema markup, I suggest reading an article about what Schema is and how to best use it. In short, it’s a system of HTML tags that help Google find specific pieces of information on your page. For example, you can tag your phone number and Google will know it’s your phone number. The benefit of using Schema is that Google understands your content better and can present it better in search. It can use schema tags to create rich snippets, populate your local business listing, and see if your content is relevant to certain types of searches. In fact, there are some types of searches that you can’t even rank for if you haven’t implemented Schema on your pages. To implement Schema on your WordPress site, it is best to use a corresponding plugin. If you’re already using Yoast for your SEO needs, you can explore Schema’s capabilities. Otherwise, you can go for a dedicated Schema plugin, such as Schema or Schema & Structured Data for WP. After you’ve implemented schema markup on your pages, make sure you see if it works using the Google Structured Data Test Tool .
12. Optimize the code
Finally, after you’ve finished building and optimizing your WordPress site, you’re likely to find that it no longer runs as smoothly as it used to. Themes, plugins, and manual customizations tend to leave a bit of a mess in your code. Over time, this mess is reflected in your performance. One of the things you can do to improve code performance is to minify your HTML, JS, and CSS files. This means removing all unnecessary formatting, things like orphaned code elements, line breaks, and comments. Although the performance improvements are often small, you can expect your code files to lose up to a third of their file size. Recommended plugins for this task are Autoptimize , WP Super Minify , and Fast Velocity Minify . Alternatively, if you don’t want to install other plugins and have a small website, you can try external code minifiers: CSS Minifier , JavaScript Minifier and HTML Compressor . Another thing you can try to optimize your code is to defer unnecessary JavaScript. Basically, rearrange the order in which different bits of code are executed on page load and move the unnecessary bits further down. This, again, can be achieved with any number of WordPress plugins, namely Async JavaScript, Autoptimize and Speed Booster Pack.
Final thoughts
It’s definitely a lot easier to optimize a WordPress site when you do it from scratch. At the same time, many of the ready-made solutions we use in WordPress (theme template) have a disadvantage in the performance of your site. I’d say that’s the main thing when trying to optimize a WordPress site — don’t be satisfied with all the plugins, sparingly install plugin software and use external tools whenever possible.
See also: